Part of a series: New product development

Summary
The strategic elements of product development, Opportunity identification and selection, Concept generation, Concept/Project evaluation, Development and Launch.
New Product Management
## Outputs vs Outcomes
Outome: Chagne in hum beh that creates customer and business value
Most good ideas failed to deliver real value due to uncertainty will the buy it? can they use it?
if features dont measure progress
Features
- dont intidate value
Business impact
- indicate value
- lagging indicator
- outside our span of control
changes in behaviour
- leading indicator
- indicate value
- within our span of control
CHEC-K Framework
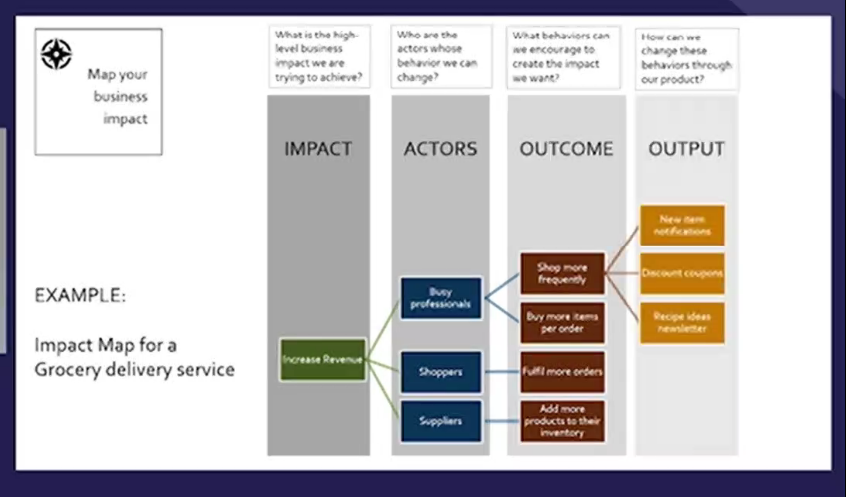
1) Map out business impact What is the high level impact you are trying to achieve? Ex. Increase revenue Who are the actors whose behaviours will change? Ex. Busy professionals, Shoppers, Suppliers What behaviours can we encourage What can we do with our product to create these changes thourhg behaviours
2) Frame your future hypothesis 3) Test your hypothesis 4) Empower your team
Features -> Change in behaviours Feature -> Hypothesis Ship -> Experiment Single -> Collective
Unknown -> Known
The strategic Elements of Product development
Between the phases, there is always go/no-go decision. These decisions are called gates, the gates can be:
- Fuzzy gate: Commonly used. this is a “conditional go”.
- Hollow gates: The Go decision is made but no financial support is provided.
Third-generation process: A flexible interpretation of the basic process, which allows overlapping phases and fuzzy gates. This flexibility is important in the development of new to the world products.
Phase 1: Opportunity Identification and Selection
We describe our process of creatively recognizing opportunities and how we came up with various opportunities in the first weeks of class. Product Innovation Charter: here we share our PIC.
- Three main streams of activity feed strategic planning for new products:
- Ongoing marketing planning.
- Ongoing corporate planning.
- Special opportunity analysis.
- From these activities, the opportunities identified can be sorted into four categories:
- An underutilized resource
- A new resource
- An external mandate
- An internal mandate
- The process of creatively recognizing such opportunities is called opportunity identification. Once and opportunity is approved, managers turn to various techniques to guide a new product people in exploiting it.
- Product innovation charter
Before you start
- Who are you? What do you do?
- Who are your customers?
- Demographics?
- Behavior traits?
- What is our core competency?
- How are we growing?
- What do we want to do?
- How much risk are we willing to take?
- Timing into market?
Identify new opportunities
The process of creatively recognizing such opportunities is called opportunity identification. Once an opportunity is approved, managers turn to various techniques to guide a new product people in exploiting it.
- Product platform planning: Build a platform that little products can come of off or take a platform and make an extension. Example: the car industry. Sony with walkman: the basic structure was the same. Boeing: many configurations for the same similar foundation for each airline.
- Greenfield markets:
- Social trends:
Corporate strengths provide direction for the team. New products in this firm will:
- Use our fine furniture designers (Herman Miller)
- Gain value by being bottled in our bottling system (Coca-cola)
- Be for babies and only babies (Gerber)
- Be for all sports, not just shoes (Nike)
- Offer genuine value (Lexus)
The PIC: Why does a firm need a new product strategy?
Set the guidelines. Points where we want to go. Setgs goals and objectives. It’s a construct on how to go forward and build new things. It is the new product team’s strategy. It is for Products (not processes). It is for innovation. A document specifying the conditions under which a firm will operate. The PIC is not the process, it’s the framework.
- To chart the new products teams direction
- To set the teams goals and objectives.
- To tell the team how it will play the game.
Most firms do have a PIC, even if they don’t call it by that name. The more detailed and specific the PIC, the higher are the firm’s innovation rates. The more specific the corporate mission and senior managment direciton is spelled out in the PIC, the better is the performance of the firms new products.
Purposes:
- Focus and integrate team effort
- Permit delegation
- Establish the size and range of the “sandbox”
Elements of a PIC:
- Business Background
- Key ideas from the situation analysis; special forces such as managerial dictate, reasons for preparing a new PIC at this time.
- What is this business about?
- Why does it exist?
- What problem is it trying to solve?
- What are your company’s core competencies?
- What are your advantages in relation to your target market’s needs, wants, and consumption trends?
- What are your company’s marketing capabilities?
- What technology currently exists?
- What is available in the market?
- Area of focus
- At least one clear technology dimension and one clear market dimension. They must match and have a good potential.
- Technology and market drivers that (1) fit and (2) have a good potential
- Goals and Objectives Of New Product (MUST BE MEASURABLE):
- What the project will accomplish, either short-term as objectives or longer-term as goals.
- profit, growth, market, status
- Short Term
- Long Term
- Guidelines
- Any “rules of the road” requirements imposed by the situation or by upper-management. Innovativeness, order of market entry, time/quality/cost, miscellaneous.
- Make sure they are specific.
- Bugdetary limitations.
- Degrees of innovativeness
- First to market
- Adaptive product
- Imitation (emulation)
- Timing
- Fist
- Quick second
- Slow
- Late
- Miscellaneous
- Avoidance of competition with certain firms
- Recognition of weaknesses
- Patentability
- Product integrity
Example of a PIC for iPad
- Background:
- Focus: Technology strengths include Apple’s OS, hardware, applications and services, product design and development skills. Marketing requirements include products on the “cutting edge” that offer seamless integration and high performance, yet are intuitive, simple and fun to use.
- Goals: Revolutionary new products should also be platforms for future products, due to the cost of “really new” product development. New pproducts should occupy the leadership position in the market.
- Special guidelines: Apple aims to be the best, not necessarily the first, in new product categories.
- The result: Apple’s first “tablet compter”, a revolutionary new product seen by many at the time as the “next big thing” No one table computer had established a dmoninant position yet, so Apple could be the standard bearer with the iPad. The plan for the future was to add capabilities and applications to future iPads.
Product portfolio
When building a new product, you are not going to build one single product. You want to make sure there is a balance of different types of products:
Objectives of product portfolio development
- Strategic alignment: Mix of products reflects the PIC
- Assessing portfolio value: commercial value of products in pipeline is maximized.
- Project balance: select products that balance the existing product line.
- Number of projects: in line with resource requirements.
Example of a portfolio diagram at a Hewlett-Packard Division
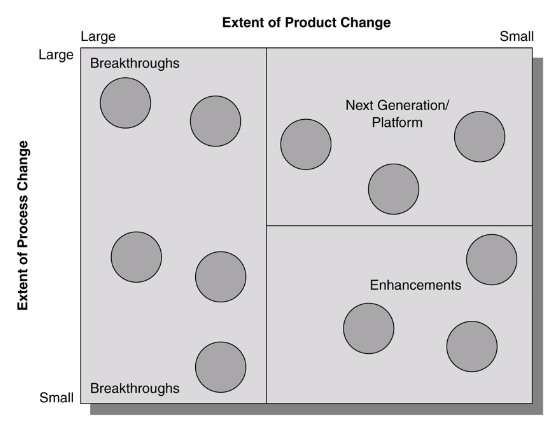
Portfolio of product types:
- Disruptive innovation
- Technology upgrade
- Product line extension
- Incremental innovation
Every single innovation does not need to be a break trough innovation.
Managing breakthrough innovation (new to the world)
- Incubation stage contrains first to market problems
- Tolerate failure but learn from it.
- Longer and much more expensive.
- Discovery-driven planning
- Forecasts and plans evolve as more information becomes available.
The role of the serial innovator
- Mid-level, technical employees who think and work differently and follow their own new products process
- Critical to firms being able to launch radical innovations successfully and repeatedly over a long period of time.
- Challenge: Identify, manage, and properly reward the serial innovator.
- Can bridte the gap between technology and market, in iterative fashion.
- Begin by undesrstanding customer problem
- Oscillate between customer need and technology solution.
- Can also bring market information
NOTE Read: Griffin, Price and Vojak, Serial Innovators: How individuals create and deliver Breakthrough innovations.
Spiral development implies many iterations between firm and customer. Useful for new-to-the-world products.
-
Products that are inventions and create a whole new market are called new-to-the-world products (Correct)
-
Identify the phase in the new product development process during which the item first acquires finite form. The concept generation phase : The development phase (Correct)
-
In the context of opportunity identification and selection, DuPont’s discovery of Surlyn, a material with hundreds of potential uses, would fall under which of the following categories? A new resource (Correct)
-
The _____ comes into play once an opportunity is approved, and managers turn to various techniques to guide new product people in exploiting it. Product Innovation Charter (PIC) (Correct)
-
In which of the following phases of the new products process is the first formal type of assessment done on new product concepts with regard to financial, technical, and marketing criteria? Concept or project evaluation phase (Correct)
-
What does the PIC NOT usually contain Background of the company Key stakeholders and responsibilities (Correct)
-
When you are evaluating products, what major concept discussed how we address and discuss the risk/reward characteristics of a new product? Product Portfolio Strategy (Correct)
Phase 2: Concept generation
Finding and Solving Customers’ problems: Scenario analysis & Determinant Gap Maps: We create a scenario analysis for some of our concepts as well as gap maps to identify opportunities. We are in the process of gathering a list of products out there for our gap analysis. Even though there are some existing products, we have confirmed that there is definitely a need for this product because existing services have just not caught on or are expensive, or require special hardware. In other words, it’s not accessible. Product concept: All that previous work led us to a product concept, where we have a need, a form, and a technology. Here is where a heavy work on market analysis happens. Our product remains the same as what we presented in our proposal. Lots of people have shown interest!
- Create new product ideas, usually called product concepts
- Problem-find-solve approach.
- Concept generation
Creativity and the product concept
What is the problem we are trying to solve?
If I had an hour to solve a problem and my life depended on it, I would use the first 55 minutes determining the proper questions to ask. Albert E.
One doesn’t just invent a finished product. An idea, yes, or perhaps a rather complete concept. It is important ot spend enough time on the idea-to-concept-to-product issue.
Roadblocks to creativity
- “Who the hell wants to hear actors talk?”
- “This ‘telephone’
- “Everything that can be invented has been invented” C.H. Duell, Commissioner, US Office of Patents
Obstancles to Idea generation
- Group think: We think we are being creative, when in reality we are only coming up with ideas that our group will find acceptable.
- Targeting error: We keep going back to the same simple demographic targets.
- Poor customer knowledge:
- Complexity:
- Lack of empathy: These same managers are also well-educated, high-income individuals accustomed to an upscale lifestyle. They may simply not understand the “typical” customer.
- Too many cooks: A small new product team works fine, but large companies especially are prone to internal competition for power and influence.
Barriers to firm creativity:
- Cross-functional diversity: Diversity leads to more creative stimulation but also to problem solving difficulties.
- Allegiance to functional areas: Team members need to have a stake in the team’s success, or won’t be loyal to the team.
- Social cohesion:
- Role of top management: Management should encourage the teams to be adventurous.
The role of management in stimulating creativity
- Recognize individuality
- Be tolerant to mistakes
- Be supportive under stress
- Competitive teams
- Idea bank of unused ideas for possible reuse
- Encourage interaction even in how offices are laid out.
Required inputs to the creation process:
- Form
- Benefit/need
- Technology
Technology permits us to develop a form that provides a benefit.
Some patterns in concept generation:
- Customer need
- Firm develops technology
- Firm envisions form
A product concept
A product concept is a verbal or prototype statemtn of :
- what is going to be changed and
- how the customer stands to gain or loose
You need at least two of the three inputs to have a feasible new product concept, and all three to have a new product.
MEthods for generating new product concepts:
- Ready-made
- new products employees
- end users
- resellers, suppliers, vendors
- Toolkit for user innovation:
- Crowdsourcing as a Creative source
- Open idea solicitation from customers
- most likely to generate modest product improvements rather than new-to-the-world products.
- Lead users as a creative source
- They have the best understanding of the problems faced, and can gain from solutions to these problems.
- Open innovation
- Accept that “not all the smart people work for us”
- It is not outsorcing! The external sources are viewed as complementary to internal sources os that innovation can be more efficient.
- Selecting the best partners is critical
Finding and Solving Customers’ problems
Problem based concept generation
Probelm analysis: General procedure
- Determine product or activity category for your study.
- Identify heavy users
- Gather set of problems associated with product strategy
- Sort and rank the problems according to severity or importance
Gethering the problems:
- internal records (routine contacts with customers)
- Direct inputs form technical and marketing departments
- Problem analysis with customers (ask them what are the problems with the current product, not what they want)
The bothersomeness technique of scoring problems:
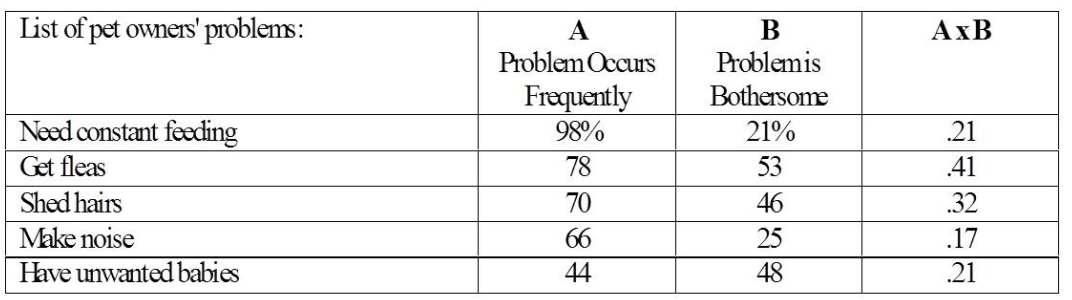
Typical questions fo problem analysis focus groups
Observation and role playing in problem analysis
Problem analysis in action
Scenario analysis
Extending vs leaping
- Extending:
- Dynamic leap scenario:
Questions:
-
According to the lecture/book, which of the following statements is true of creative people? They tend to be creative throughout their lives and never become uncreative. (Correct)
-
In the context of barriers to firm creativity, strong interpersonal ties between team members tend to lead to: lack of creative abrasion. (Correct)
-
Which of the following statements is true of a focus group? A focus group is designed to yield an exploratory and depth-probing type of discussion. (Correct)
-
With reference to scenario analysis, in _____ studies, the focus is on what changes must be made between now and then if the leap scenario is to come about. dynamic leap (Correct)
-
A group ideation technique put forth by Alex Osborn that involves a process where one person presents a thought, another person reacts to it, another person reacts to the reaction, and so on is called brainstorming.
Solving the problem
Principles of brainstorming:
- deferral of judgement
- quantity breeds quality
Rules for a brainstorming session:
- no criticism allowed
- Freewheeling – the wilder the better
- Nothing should slow the session down.
- Combination and improvement of ideas
Electronic brainstorming:
- Supported by GSS (group support sytems) software.
- can handle larger size groups
- contributions are projected on screen and also recorded
Online communities
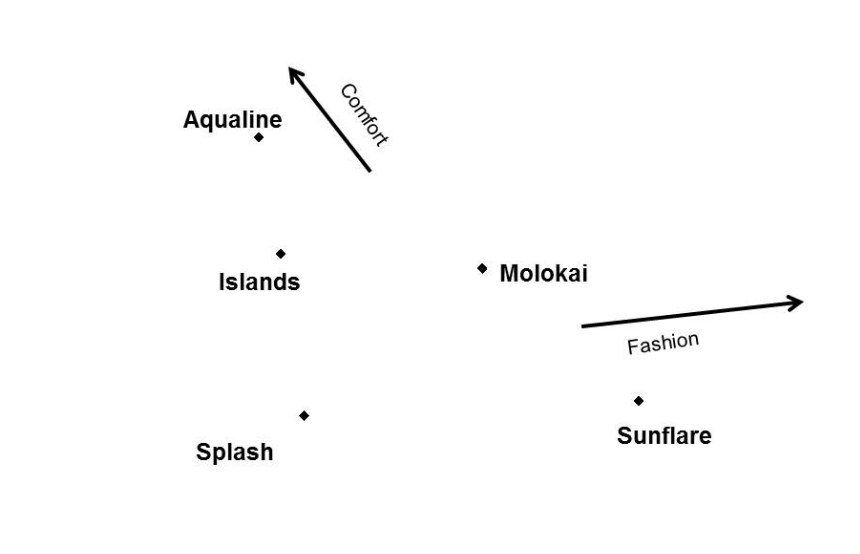
Analytical attribute approaces: Introduction and Perceptual mapping
Basic idea: products are made up of attributes – a feature product change must involve one or more of these attributes.
Theoretical sequence: feature permits a function which provides a benefit.
- Features: What the product consists of.
- Functions: How a product works. What it does.
- Benefits: How the product provides satisfaction to the user.
Types of gap analysis:
- Determinant gap map: produced from managerial input/judgement on products)
- AR (Attribute rating) perceptual gap map: based on attribute ratings by customers. You go to customers, and have them evaluate the product.
- OS (Overall similarities) perceptual map: based on overall similarities rating by customers. Some things are hard to define, but if you group product based on these rating, you can start figuring out how similar products are from each other.
Determinant gap map
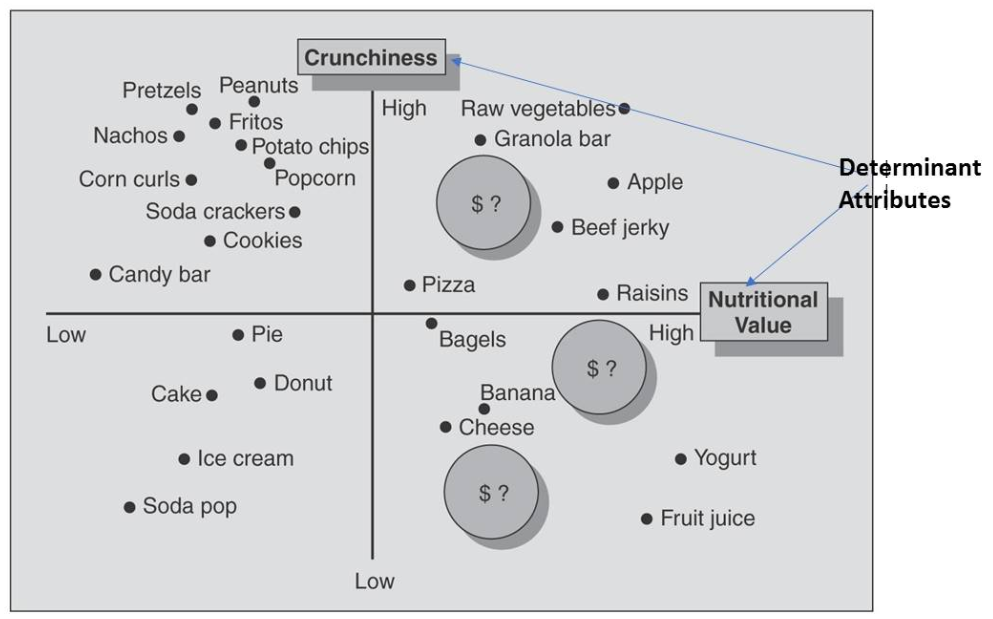
Creating a GAP map in Excel
Attribute Rating (AR)
Consumers have ranked this. This how people percieve the product. PErception does not equal reality.
Overall similarities (OS)
Data reduction using multivariate analysis
- Factor analysis: Reduces the original number of attributes to a smaller number of factors, each containing a set of attributes tha “hang together”.
- Cluster analysis: Reduces the original number of respondents to a smaller number of clusters based on their benefits sought, as revealed by their “ideal brand”.
All gap mapping is controversial.
It’s aimed at discovering gaps, not demand. Gaps might exist for a reason.
Questions:
- How are the values in a Determinant Gap Map (as discussed in chapter 6) created? Manager’s judgment call (Correct)
- What is NOT defined as kind of attributes that you can quantify in analytical attribute techniques? Failure (Correct)
Phase 3: Concept/Project evaluation
We introduce the concept evaluation system, and the risk/payoff matrix. Concept testing: We run a concept testing study, Product protocol: We present our protocol, (to the extent possible, must be about the benefits the new item is to yield, not the features the new item is to have!) When this is done, we will have a crystal clear description of who will buy this product and why.
- Before development work can begin on new ideas, they need to be evaluated, screened, sorted out. Screening or pretechnical evaluation.
- Quick looks … to complete discounted cash flows and net present value
- Full-screen
- If the decision is to go ahead, the evaluation turns into project evaluation, where we no longer evaluate the idea, but the plan we propose for capitalizing on that idea.
- Quality Function Deployment (chapter 12)
- Product description or product definition or product protocol: Means a kind of agreement between the various groups the various groups before the extensive technical work gets under way. The protocol should, to the extent possible, be benefits the new item is to yield, not the features the new item is to have.
Questions:
-
What is a Pothole evaluation system? Everything is tentative - just keep going while revising the plans along the way Identify the damaging problems and only focus on them in the evaluation (Correct)
-
What does the A-T-A-R stand for in the ATAR model Awareness - Trial - Availability - Repurchase (Correct)
-
The assumption behind the use of conjoint analysis is that: a product can be represented as a set or bundle of attributes. (Correct)
-
True or False: Respondents in a “conjoint research project” need to consciously understand how they rank product attributes. False (Correct)
Phase 4: Development
The item or service itself, (we will try to really, as in real life, prototype this) if possible we describe the results of our Product Use Testing The marketing plan for it. We propose a promotional plan which is appropriate for the audience, resources, and strategy for the launch. A business (or financial) plan. We discuss the financial analysis, which is still not firm, but it is good enough to assure that this project will be worthwhile. The financials will gradually be tightened during the launch phase. Gate evaluation. By now we should have financials, product use results, marketing campaigns. Again, evaluate the gates and decide if we are to move on to launch.
This is the phase during which the item acquires finite form- a tangible good or a specific sequence of resources and activities that will perform an intangible service. Marketing plan is sketched and gradually fleshed out.
- Resource Preparation: it may need special training, new reward systems, revisions in the firms usual project review system and special permissions.
- The major body of effort: The actual development of:
- The item or service itself
- The marketing plan for it
- A business (or financial) plan
- The product (or concept) stream involves industrial design and bench work (goods) or systems design (serivces) , prototypes, product specifications, and so on. It culminates in a product that developers hope is finished: produced, tested, and costed out.
- Marketing planners are busy making periodic market scans (to keep up with the changes) and making marketing decisions as early …. First strategic, then tactical.
- Comprehensive business analysis: The financial analysis is still not firm, but it is good enough to assure managmeent that ithis project will be worthwhile. The financials will gradualy be tightened during the launch phase, and where the actual Go/No Go point is reached varies.
Questions:
-
What tool helps you eliminate many ideas before concept testing even begins? Product Innovation Charter (PIC) (Correct)
-
What is NOT a stated purpose of concept testing Design effective marketing material for campaign (Correct)
-
True or False - Focus groups are not a great tool to use in concept testing because they are not quantitatively robust: False (Correct)
-
True or False - A good screening process will eliminate subjective judgement from the evaluation FALSE (Correct)
- The primary purpose of the full screen is to obtain the information required for developing the product innovation charter. estimate the feasibility of technical and commercial accomplishments. (Correct)
-
Star Inc. has restricted its budget for developing new products to $20,000. It automatically vetoes a proposed product if the product scores poorly on the factor of budget during the screening process. This factor is known as a _____ factor. culling (Correct)
- Which of the following is an objective of full screening? To encourage cross-functional communication (Correct)
Phase 5: Launch
Here we describe the results of market testing (if we have a prototype) and present a strategy for launch. The final gate. We make a recommendation if this product should move on or not based on the market test. Retrospection. We talk about what are our KPIs and how to collect telemetry from the field to know if we are successful or not. Launch (or commercialization) has described that time Includes last few weeks or months before and after the product is launched. Manufacturing is doing a gradual scale-up output. The critical step is to market test, and managers hope any problems discovered are dixable between dress rehearsal and opening night. (chapter 18)
Questions:
-
In order to calculate the net present value that might be associated with a proposed product, it is necessary to: create a sales forecast (Correct)
-
Which of the following serves as the basis of many simulated test markets? The cumulative expenditures curve The A-T-A-R model (Correct)
-
Which of the following forecasting tools is commonly used for durable goods and is based on the diffusion curve of new products through a population? The Bass model (Correct)
-
_____ is a technique used by Toyota to get cooperation across functional areas, to speed up integration, and to focus the team. The Oobeya Room (Correct)
-
_ has been defined as a complete set of customer wants and needs, expressed in the customer’s language, organized the way the customer thinks about, uses and interacts with the product, and prioritized by the cust. in terms of importance and performance. Voice of the customer (Correct)
-
Engineering characteristics and customer attributes are part of the HOQ grid (Correct)
-
Question #7 The first general purpose of a product proposal is to: identify the target audience and the benefits offered to them. (Correct) specify whether the offering is a tangible product or an intangible service. (Correct) ensure that all tax payments with regard to the product are paid on time. (Correct) specify what each department will deliver to the final product that the customer buys. (Correct)
Which of the following is true of market-driven innovation? The main purpose of design in market-driven innovation is to modify the product so that it meets customer expectations. (Correct) In market-driven innovation, new meanings and new technologies are pushed forth. In market-driven innovation, design is of primary importance, and it takes on the leadership role. The main role of design in market-driven innovation is to modify the product so that it can accommodate the performance characteristics. DarkBerry Inc., a cellphone manufacturer, manufactures products that share common design features that make them unique, yet at the same time familiar. All of DarkBerry’s cellphones have a sleek appearance and an elegant design. These products can be described as being designed for the environment. described as being designed to build or support corporate identity (Correct) described as being designed for ease of manufacture. described as being designed for for price promotion. ___ are technical people who convert styling into product dimensions or specifications. Industrial mechanists Risk incorporators Design engineers (Correct) System analysts The most heavyweight of the three matrix structures is the: project matrix structure. (Correct) functional matrix structure. balanced matrix structure. departmental matrix structure. In which of the following organizational options does the project manager have the least amount of power? Project matrix option Venture option Functional matrix option Functional option (Correct) Those people who are involved in managing functional clusters comprise the ___ team. core. (Correct) ad hoc. product champions. extended.
Implementation of strategic plan
The launch cycle
Launch tactic:
- Promotion
- Advertising
- Coupons
- Publicity
- Sampling
- Beta test sites
- Sales and distribution
- Shows/demonstrations
- Technical support
- Distribution structure
- Intensity of coverage
- Distribution incentives
- Pricing
- Introductory pricing
- Price administration
- Product
- Breadth of assortment
- Timing
- Product deletion
- Preannoucing
Preannouncement
- Getting to be popular, and very creatively managed.
- Far from the old days of “tease the public”
Beachhead:
- Refers to the heavy expenditure needed to overcome slaes inertia (“getting the ball rolling”)
- Begins with the annoucement
Launch tming and lean launch:
- Flexible supply chain system allowing the firm to respond rapidly to sales changes
- Lean launch gives the firm flexibility in launch timing.
Postponement, refers to delaying finalization of product form and identity until last possible moment. Two categories:
- Time postponement:
- Form postponement: lock in product design as late as possible.
Lean lauch: Firm needs good information technology system in place to track sales and replenish raw material and inventory.
Copy strategy statement:
- Communications tools used at launch will have certain deliverables.
- The way in which the firm communicates these deliverables to the advertising and promotion creative poeple is the copy strategy statement.
- Typical contents:
- The market segment targeted
- The product positioning statement
- The communications (promotion) mix
- The major copy points to be communicated.
- Often stated as attributes (features, functions, benefits) but not limited to these.
Typical examples of copy points:
- “The provider of this insurance policy is the largest in the world”
- “This new line of housewares is now available at target”
- This cellular phone has no geographic limitation”
Motivate distributors:
- Icrease distributors unit value.
- Increase distributors unit margin
- Reduce distributors cost of doing business
- Change distributors attitude totward the line.
Barriers to trial:
- Lack of interest in the claim.
- Comptitive ties.
- Lack of belief in the claim.
- Routines
- Rejecting something negative about product.
- Cost
- Complacency
Market testing
This is not testing the product or how it lands, its testing what is going on in the market. How well your activities to promote your product are going to work.
The evaluation of the product together with its marketing plan.
Product use testing: does this product work as expected. Market testing: does our launch, do our marketing activities work as we planned.
Two key values obtained from market testing:
- Solid forecasts of dollar and unit sales volume.
- Diagnostic information to allow for revising and refining any aspect of the launch.
IT will tell you if there is anything we can do to tweak the launch of the product.
Decide wether to market test:
- Any special twists on the launch?
- What information is needed?
- Costs
- Nature of marketplace
- Capability of testing methodologies
Types of information that might be lacking:
- Manufactuing process: can we ramp-up from pilot production to full scale easily?
- Vendors and resellers: will they do as they have promised in supporting the launch?
- Servicing infrastructure: adequate?
- Customers: will they buy and use the product as expected?
- Cannibalization: waht will be the extend?
Methods of market testing
Pseudo Sale:
Speculative Sale: If we make this product available as I have described it, would you buy it?
Simulated test market:
- Create a false buying situation and observe what the customer does.
- Follow-up with customer later to assess likely repeat sales.
- Often used for consumer nondurables.
The test market:
- Several test market cities are selected
- Product is sold into those cities in the regular channels and advertised at representative levels in local media.
- Once used to support the decision whether to launch a product, now more frequently used to determine how best to do so.
Pros and Cons of Test Marketing:
- Advantages:
- Risk reduction
- Strategic improvement
- Disadvantages
- Cost
- Time (hurt competitive advantage)
- Competitor can disrupt test market
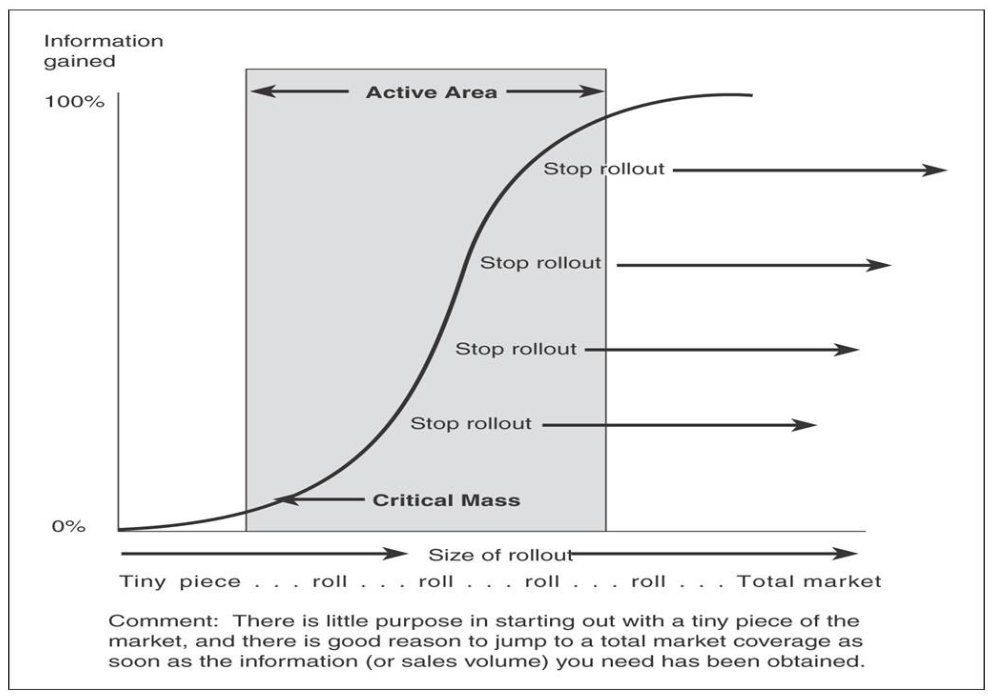
Patterns of information gained during rollout
New Product Marketing
Other
- Dr. Silver. Inventor of Post-it at 3M.
- Sir James Dyson
Market research tools:
- Creativity sessions
- Tradeoff analyses
- Concept tests
- Voice of the customer
- Alpha and beta testing
- Test markets
Firms with a global innovation culture:
- Procter & gamble
- Apple
- Ikea
Not all new products are planned:
- Microwave ovens
- Aspartame
- ScotchGard fabric protector
- Teflon
- Penicillin
- X-rays
- Dynamite
New Products:
- New to the world products: Inventions that create a whole new market.
- New to the firm products: Take a firm into a category new to it.
- Additions to existing product lines: Line extensions and flankers that flesh out the product line in current markets.
- Improvments and resvisions to existing products (Updates)
- Cost reductions: New products that provide similar performance, but at a lower cost.
- Repositionings: Products that are retargeted for a new use, market or application.
Top innovatorssuch as inten and Gillette stay focused and committed to innovation as a long-term strategic goal. Without such focus, firms can fall back to “tweaking” existing products.
Resources
Visions magazine: Look at Visions magazine: Connecting Innovators Worldwide. PDMA is the number 1 global source of end-to-end product management and product development knowledge, wisdom, experience, and expertise. PDMA has been advancing product managers and product teams for over 43 years. We are different from for-profit training and certification companies. PDMA’s membership and body of knowledge is powerful and made up of expert practitioners, academics, teams, chapters, and corporations.
Procter & gamble case:
- Situation assessment
- PIC recommended a strategic focus on products for the face (?) - other opportunities would not be pursued.
- If already several eye makeup products on the market, they would not immediately launch another. Managemnt called this an “initiative rhythm” for product launch.